Nvidia's AI blueprint accelerates smart city development with advanced digital twins.
Revolutionizing urban life: Nvidia's AI blueprint leverages digital twins to create smarter, safer, and more sustainable cities.
June 11, 2025
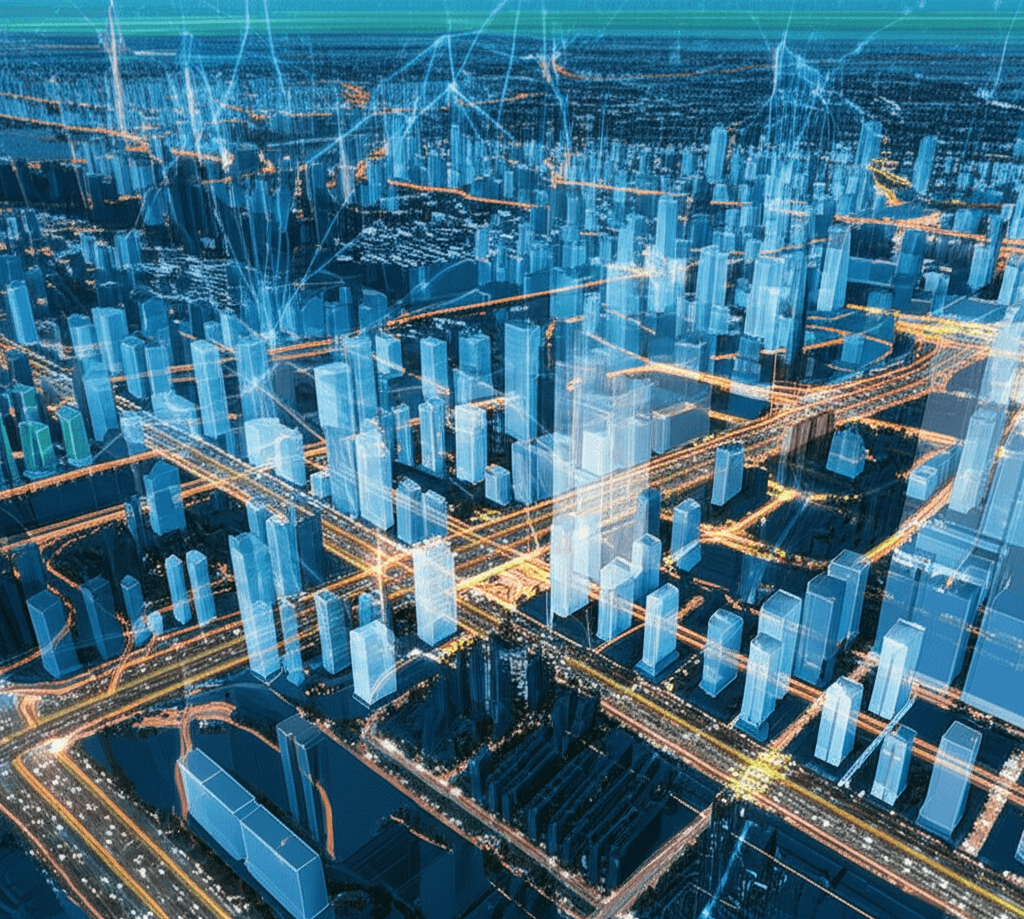
Nvidia is pioneering new frontiers in the development of smart cities, showcasing its Omniverse Blueprint for smart city AI, a framework designed to facilitate the creation of urban digital twins and the testing of AI agents within these virtual environments. This initiative, highlighted at Nvidia GTC events including a recent showcase in Paris during VivaTech, aims to address the complexities of urban planning and management as global urban populations are projected to double by 2050.[1][2][3][4] The blueprint integrates several key Nvidia technologies, including Omniverse for physically accurate digital twin creation and simulation, Cosmos for generating synthetic data to train AI models, NeMo for curating data and fine-tuning vision and large language models, and Metropolis for deploying video analytics AI agents.[2] This comprehensive software stack empowers developers to build and test AI-driven solutions for optimizing city operations, enhancing sustainability, and improving the quality of life for urban residents.[2][1]
The core of Nvidia's smart city strategy lies in the power of digital twins – virtual replicas of physical urban environments that mirror real-time changes.[5][6] These SimReady, photorealistic environments, built using Omniverse, allow for extensive simulation and testing of AI agents before deployment in the real world.[1][2] This capability is crucial for anticipating the impact of new technologies and policies, optimizing resource allocation, and planning for various scenarios, including emergency response and infrastructure upgrades.[2][5][6] For instance, SNCF Gares & Connexions, which operates 3,000 train stations in France and Monaco, has utilized digital twins and AI agents for real-time operational monitoring, simulating emergency responses, and planning infrastructure improvements, leading to better predictive maintenance and energy management.[2][3] Similarly, Kaohsiung City in Taiwan, in partnership with Linker Vision and AVES Reality, is using this technology to analyze up to 50,000 video streams in real-time with generative AI to understand and narrate complex urban events like floods and traffic accidents, significantly reducing incident response times.[1][2][3]
A critical component of the blueprint is the ability to train and refine AI models effectively. Nvidia Cosmos plays a vital role here by enabling the generation of large-scale synthetic data.[2] This is particularly important for training AI models to handle a wide variety of situations, including those that are rare or dangerous to replicate in the real world, such as extreme weather events or traffic accidents.[1][7] The Nvidia NeMo platform further assists in curating high-quality data and fine-tuning vision language models (VLMs) and large language models (LLMs), enhancing the accuracy and capabilities of AI agents designed for smart city applications.[2] These AI agents, often deployed through the Nvidia Metropolis framework, can then process vast amounts of video and sensor data from city infrastructure to provide actionable insights.[2][8] Metropolis offers a suite of tools and an application framework for video analytics, enabling functionalities like traffic management, public safety, and operational efficiency improvements.[8][9][10] For example, the city of Palermo in Sicily is leveraging AI agents and digital twins to enhance public safety by processing extensive video data for real-time event alerts.[3]
The implications of Nvidia's Smart City AI Blueprint for the AI industry are substantial. It provides a standardized yet flexible platform for a diverse ecosystem of partners, including software vendors, urban planners, and infrastructure developers, to collaborate and innovate.[2] Companies like Bentley Systems, Cesium, Younite AI, and K2K are among the early adopters leveraging this blueprint to develop and deploy their smart city solutions.[2][11] Younite AI, for instance, is using the blueprint to accelerate its development pipeline for large-scale urban simulations and real-time IoT data integration.[2] K2K is utilizing Nvidia AI Blueprints, including the video search and summarization (VSS) blueprint, to create AI agents capable of understanding activities within video feeds for applications like traffic optimization and environmental monitoring.[11] This collaborative approach, built upon open standards like Universal Scene Description (USD) for Omniverse, fosters interoperability and allows for the integration of various tools and data sources.[6][12] Furthermore, the emphasis on generating synthetic data addresses a key bottleneck in AI development – the availability of large, diverse, and well-annotated datasets.[8][13][12] This can significantly accelerate the training and validation of AI models for complex urban environments. The ability to simulate and test AI agents in a risk-free virtual environment before real-world deployment also promotes safer and more reliable AI systems.[5][6]
Looking ahead, the continued development and adoption of such blueprints are poised to transform how cities are designed, managed, and experienced. The focus on "physical AI" – AI that interacts with and understands the physical world – opens up possibilities for more autonomous and intelligent urban systems.[2] This extends beyond just monitoring to enabling predictive maintenance, optimizing energy consumption, streamlining transportation networks, and improving emergency response.[2][5][14] The expansion of AI capabilities, including generative AI for narrating complex events and enhancing contextual understanding, will further empower city officials and residents with timely and relevant information.[1][7] However, the widespread implementation of these technologies also brings challenges that need careful consideration, including data privacy, security, the cost of infrastructure, the need for a skilled workforce, and ensuring public acceptance.[14] Addressing these concerns will be crucial for realizing the full potential of AI in creating more sustainable, resilient, and livable cities of the future. Nvidia's ongoing partnerships with governments, telcos, cloud providers, and research institutions aim to build out the necessary infrastructure and skills base to support this evolution.[4][15][16]
Sources
[2]
[4]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12]
[14]
[15]
[16]