Google Unveils 'USB-C for AI,' Integrating MCP for Seamless Agent Connectivity
Google embeds AI's "USB-C" protocol, empowering developers to build smarter, interoperable AI agents with ease.
December 11, 2025
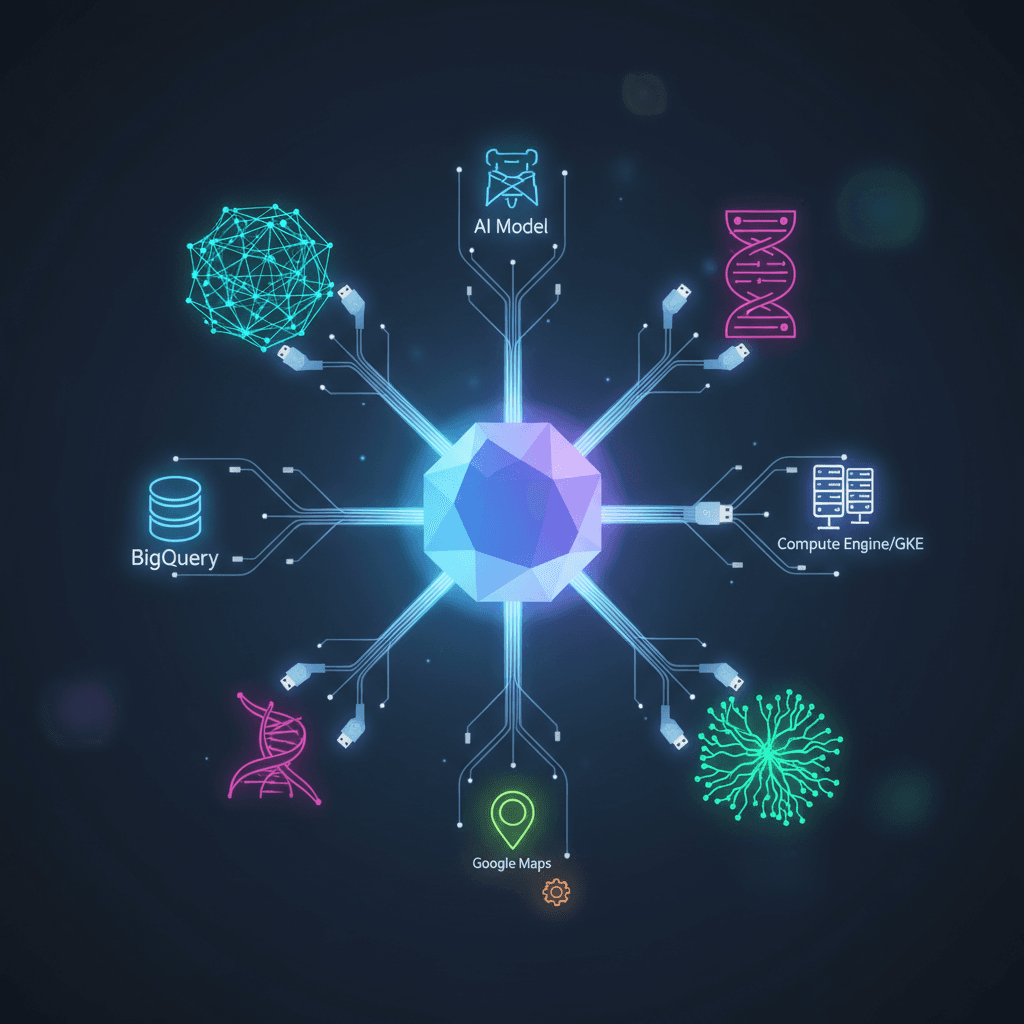
In a significant move toward creating a more open and interconnected artificial intelligence ecosystem, Google is deeply integrating Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP) into its core cloud infrastructure. The technology giant has announced the release of fully-managed, remote MCP servers, designed to standardize and simplify how AI models, often called agents, connect with data and tools across Google's vast suite of services.[1][2] This initiative effectively lowers the barrier for developers, enhances the capabilities of AI agents, and signals a broader industry shift away from fragmented, proprietary integrations toward a more interoperable future. The move is poised to accelerate the development of sophisticated AI applications by allowing models from various providers, including Anthropic and OpenAI, to seamlessly interact with Google's powerful cloud services.[3]
At its core, the Model Context Protocol is an open standard, first introduced by AI safety and research company Anthropic, that acts as a universal translator between large language models and external data sources or tools.[4][5] Often likened to a "USB-C for AI," MCP provides a standardized communication framework that eliminates the need for developers to build custom, one-off connections for every tool or data source an AI model needs to access.[1][2] Before the widespread adoption of such a standard, connecting AI models to real-world information was a complex task, creating what Anthropic described as an "N×M" data integration problem, where each new model required a unique integration for every data source.[4] MCP solves this by establishing a client-server architecture where AI applications can discover and interact with available tools and data through a consistent interface, enabling them to perform complex, multi-step tasks that go beyond their pre-trained knowledge.[4][1] This allows AI agents to become more dynamic and useful, capable of accessing real-time information and performing actions in the real world.[4]
Google's embrace of MCP goes beyond simple support, embedding it directly into the fabric of Google Cloud. The company is launching fully-managed, remote MCP servers, which means developers no longer need to install, manage, and maintain their own local servers—a process that was often burdensome and led to fragile implementations.[1][2] Instead, developers can now connect their AI agents to a globally consistent and enterprise-ready endpoint to access Google Cloud services.[1] The initial rollout includes managed MCP servers for key services such as Google Maps, BigQuery, Compute Engine, and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).[3][2] This integration allows an AI agent to perform tasks like querying an enterprise database with BigQuery to forecast revenue, cross-referencing Google Maps to find optimal retail locations, or even managing cloud infrastructure directly through natural language commands.[1][3][6] Furthermore, Google is extending this capability to enterprise customers' own systems through its Apigee API management platform, allowing organizations to expose their existing APIs as secure and governable MCP tools for their AI agents.[1][7]
The strategic implications of Google's deep MCP integration are far-reaching, impacting developers, businesses, and the competitive cloud landscape. For developers, the move drastically reduces complexity and accelerates the development of powerful, agentic AI applications.[8][1] By providing a standardized, secure, and managed connection to its services, Google is freeing up developers to focus on innovation rather than infrastructure plumbing. For the broader AI industry, this represents a significant step towards interoperability and an open ecosystem.[9] Google's commitment is further solidified by its role as a founding member of the new Agentic AI Foundation (AAIF), alongside Anthropic, OpenAI, Microsoft, and AWS, which will house MCP as a vendor-neutral standard.[10] This collaboration among fierce competitors underscores a collective recognition that open standards are necessary to prevent vendor lock-in and foster a healthy, competitive market where AI agents can work seamlessly across different platforms and tools.[10][11] This move may also enhance Google Cloud's competitive position against rivals like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure by attracting developers who prioritize open, flexible, and interoperable AI development environments.
In conclusion, Google's decision to weave the Model Context Protocol into the core of its cloud platform is more than a technical upgrade; it is a strategic endorsement of an open and collaborative future for artificial intelligence. By providing managed MCP servers, Google is not only simplifying the creation of next-generation AI agents but also championing the interoperability that will be crucial for the technology to reach its full potential. This initiative tackles significant development hurdles, strengthens the entire AI ecosystem through a commitment to open standards, and positions Google Cloud as a central hub for building and deploying intelligent, interconnected AI systems. As AI continues to evolve from isolated models to collaborative agents, standardized protocols like MCP, backed by industry giants, will form the essential connective tissue for a more capable and integrated technological future.